Teneligliptin 20mg + Dapagliflozin
Introduction
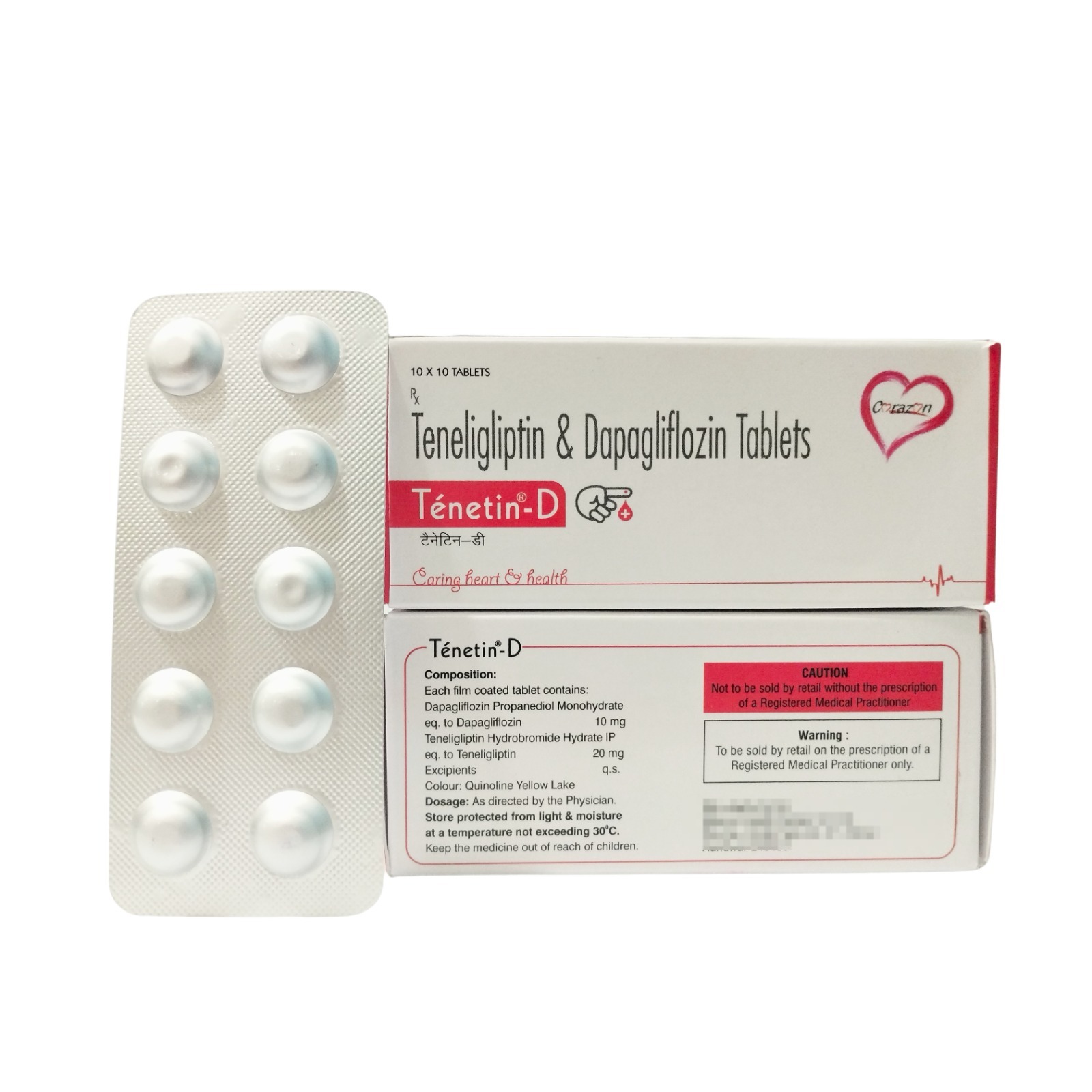
Tenetin-D is a fixed-dose oral antidiabetic combination containing Teneligliptin 20 mg (a DPP-4 inhibitor) and Dapagliflozin 10 mg (an SGLT2 inhibitor).
It is used for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in patients who do not achieve adequate glycemic control with single therapy, diet, and lifestyle modifications.
🔹 Indications
-
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM).
-
As an add-on therapy in patients inadequately controlled on diet, exercise, or monotherapy.
-
May provide additional benefits in weight reduction and cardio-renal protection (dapagliflozin component).
🔹 Dosage
-
Adult dose: 1 tablet (Teneligliptin 20 mg + Dapagliflozin 10 mg) once daily, with or without food.
-
Adjustment: Dose adjustments usually not required in mild renal or hepatic impairment, but contraindicated in severe cases.
-
Always taken as per physician’s prescription.
🔹 Mechanism of Action (MoA)
-
Teneligliptin:
-
Inhibits DPP-4 enzyme → increases incretin hormones (GLP-1 & GIP).
-
Enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion, reduces glucagon release.
-
Improves postprandial and fasting blood glucose.
-
-
Dapagliflozin:
-
Selective SGLT2 inhibitor in the renal proximal tubules.
-
Prevents reabsorption of glucose in kidneys → increases urinary glucose excretion → lowers blood sugar independently of insulin.
-
✅ Dual action: One insulin-dependent (Teneligliptin) + one insulin-independent (Dapagliflozin).
🔹 Pharmacology
1. Absorption
-
Teneligliptin: Rapidly absorbed, peak plasma concentration in ~1–2 hrs, bioavailability ~90%.
-
Dapagliflozin: Peak plasma levels in ~2 hrs, bioavailability ~78%.
2. Distribution
-
Teneligliptin: Plasma protein binding ~60–70%.
-
Dapagliflozin: Plasma protein binding ~90%.
3. Metabolism
-
Teneligliptin: Metabolized mainly by CYP3A4 and FMO3.
-
Dapagliflozin: Metabolized primarily via UGT1A9 to inactive metabolite.
4. Excretion
-
Teneligliptin: ~45% via urine, ~55% via feces.
-
Dapagliflozin: Excreted mostly in urine as metabolites.
🔹 Precautions
-
Renal function monitoring (dapagliflozin can reduce renal threshold for glucose).
-
Risk of genital mycotic & urinary tract infections (dapagliflozin).
-
Monitor for hypoglycemia when combined with insulin or sulfonylureas.
-
Risk of volume depletion & hypotension due to osmotic diuresis.
-
Rare cases of pancreatitis (DPP-4 inhibitors).
-
Elderly patients: Use cautiously due to renal and dehydration risks.