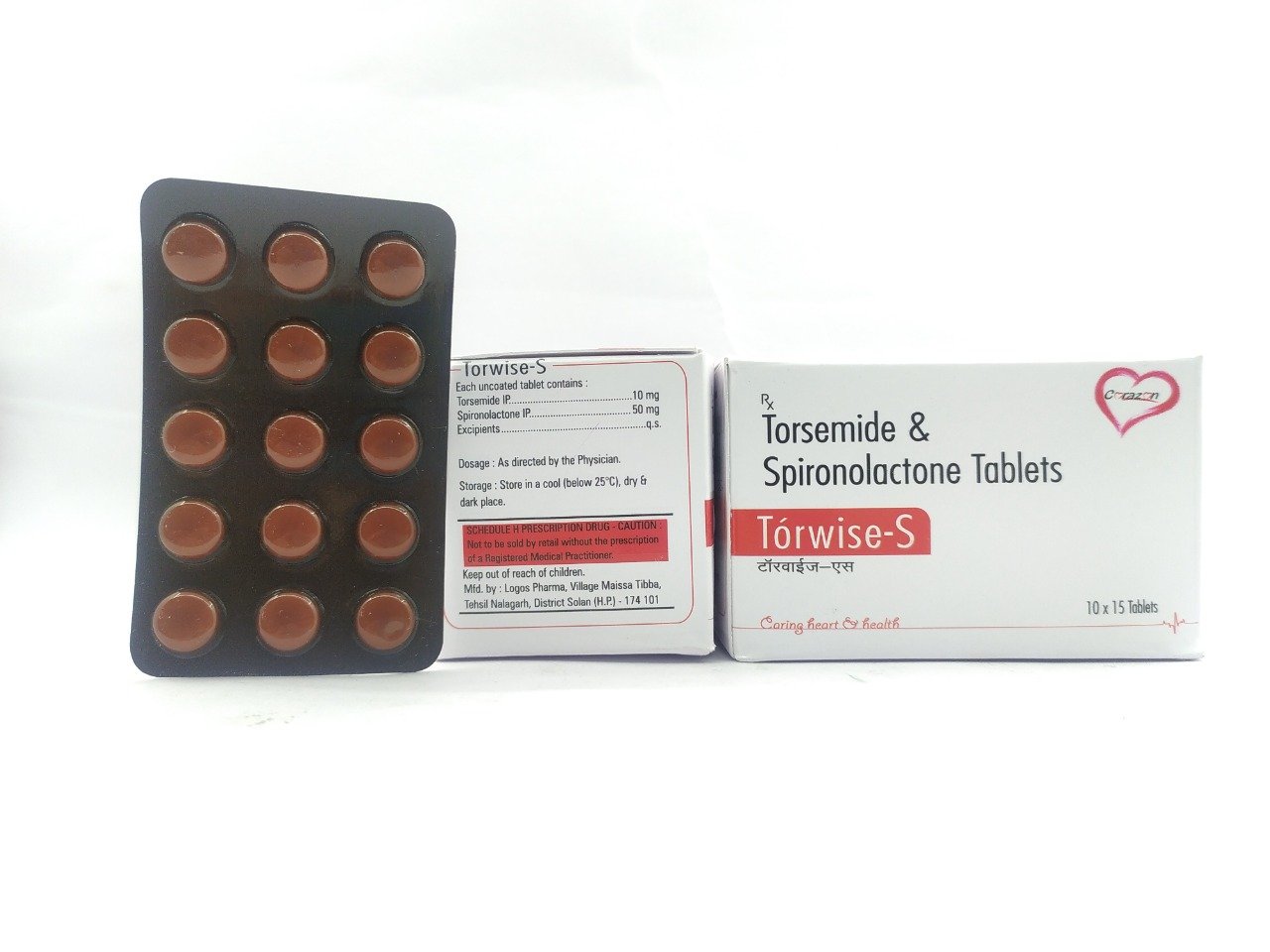
Torsemide Spironolactone 40mg 50 mg Tablet
The combination medicine, Spironolactone+Torasemide is used in the treatment of Edema. The active ingredients act on different parts of the kidney to remove excess water and certain electrolytes while marinating the potassium balance in the body. Torsemide reduces the extra fluid in the body (edema) caused by conditions such as heart failure, liver disease, and kidney disease. The drug is also indicated for high blood pressure and prevents strokes, heart attacks, and kidney problems. The medicine acts as a water pill (diuretic) that increases urine production and excrete excess water and salt.
Take the medicine as per the prescribed dosage and duration recommended by a doctor. It is suggested to take the medicine 4 hours before going to bed to avoid waking up at night to urinate. The dosage depends on the health condition and response to the treatment. Stay regular with the treatment and do not skip doses. Some people may observe symptoms such as dizziness, electrolyte imbalance, muscle cramps, weakness, unusual tiredness, confusion, nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, and irregular heartbeats. Inform your doctor if you are allergic to the active ingredient or similar medicines. Also, inform the doctor about your medical history and current health conditions.
Contraindications of Spironolactone+ Torasemide Tablets
Avoid taking this medicine, if you are suffering from any of the following mentioned diseases:
- Anuria
- Acute renal insufficiency
- Hepatic coma and pre-coma
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Patients taking aminoglycosides or cephalosporins
- Kidney dysfunction due to drugs that cause renal damage
- Patients with high potassium levels hyperkalemia)
- Addison's disease
- Children with moderate to severe renal impairment
Uses of Spironolactone+ Torasemide Tablets
Combination medicine is used in the treatment of the following health conditions:
- High Blood Pressure
- prevent strokes, heart attacks, and heart failure
- Edema
Side Effects of Spironolactone+ Torasemide Tablets
Usually, the medicine has mild to temporary side effects that resolve over time. If the side effects persist or get severe with time, immediately consult your doctor. The side effects are individualistic and depend on the current health conditions and response to the medication. The list of side effects is given below:
- Dizziness
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Headache
- Inflammation of the nose
- Muscle pain
- Gastrointestinal disturbance
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Decreased white blood cell count (lymphocytes)
- Low blood platelets
Precautions and Warnings
- Pregnant women should avoid taking this medicine and consult their doctor if it is necessary to the tablets.
- Avoid consuming alcohol when taking tablets as it may worsen the conditions.
- Avoid driving or performing any mental activity that requires you to mentally concentrate as the Spironolactone+ Torasemide tablets cause’ dizziness.
- Spironolactone+ Torasemide Tablets may cause your blood sugar levels to fluctuate hence, regularly check your blood sugar if you have diabetes and take these tablets.
- Store the tablets in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Keep the medicine away from children and pets. Properly dispose of expired and discarded medicines.